When T-Mobile took its T-Satellite service live during the summer, it teased the ability for developers to adapt their apps to work within the strict data limits required over satellite connections. Then, several apps were able to jump the gun and start working with the Starlink-based service at the launches of the Pixel 10 Pro and the iPhone 17. Now T-Satellite is open to any app configured to work with the network — with a few surprises I didn’t think we’d see so early.
Get ready to video chat with your friends from the middle of nowhere… Or prepare to be trapped by your friends who want to video chat no matter where you are.
Don’t miss any of our unbiased tech content and lab-based reviews. Add CNET as a preferred Google source.
T-Satellite breaks some Earth-bound limitations
T-Mobile isn’t the first company to connect a smartphone to a satellite network. Recent iPhone, Samsung Galaxy and Google Pixel models equipped with the proper hardware can talk to satellites when out of cellular range to access emergency services, text using the Messages app and send a location via Find My. But those are primarily based on sending short bursts of data, which is essential when communicating line-of-sight with satellites that are thousands of miles overhead and limited in their bandwidth capacities.
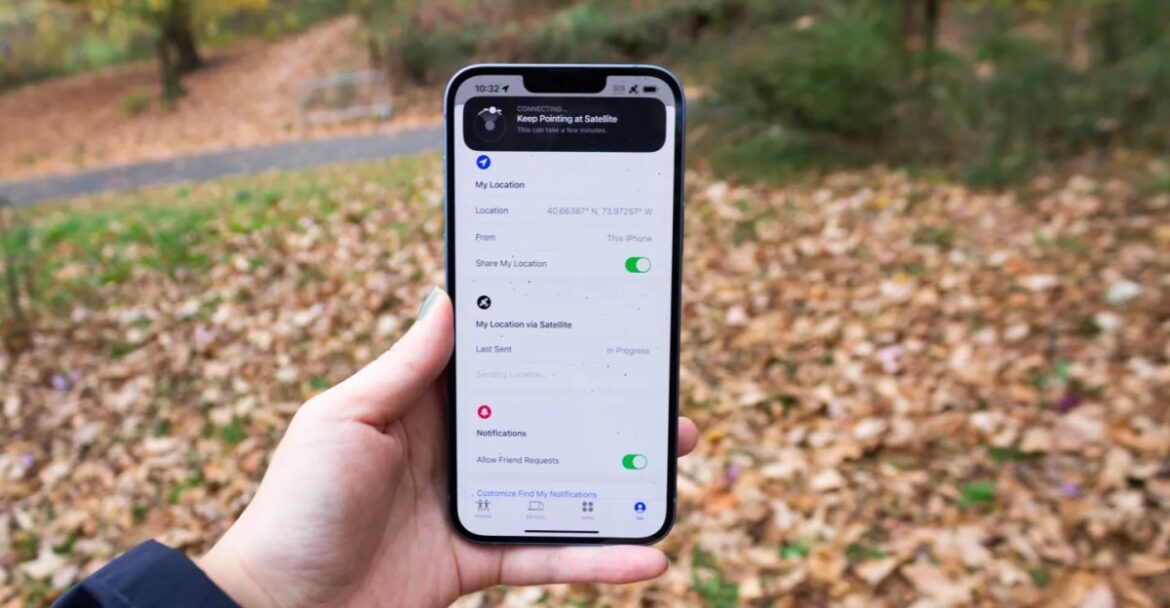
T-Satellite accesses a network of 657 Starlink satellites dedicated to cellular service using a band of cellular spectrum that works with most phones made during the last four years, according to T-Mobile. The company has also offered the service to customers of other providers for $10 a month. It shares the same text-centric limitations as the other companies, with the added ability to send and receive images using Multimedia Messaging Service.
With today’s announcement, T-Mobile is setting some of those limitations aside. In the WhatsApp app, for example, you can send texts, images, voice memos and video messages, which still fit (barely?) within the send-small-bursts-of-data model. WhatsApp now also supports live audio and video chats to other people using WhatsApp, but you can’t use it to make phone calls, emergency calls or texts.
Another example is the X app (formerly Twitter), which lets you scroll your feed and post text, photos, GIFs or videos. It also has the option to download high-resolution media when you need more detail.
Watch this: Hands-On with T-Mobile’s T-Satellite Service
01:55
Launching app data access
According to Jeff Giard, vice president of strategic partnerships at T-Mobile, getting to this point was largely due to customer feedback during the lengthy T-Satellite beta period while the Starlink constellation was still being completed. “We started seeing [customer feedback] start to shift to ‘Hey, this is awesome. I want more,'” he said. “So we started focusing on how do we enable great experiences on apps in an environment where it’s not our blazing-fast terrestrial network?”
Because T-Satellite is based on the LTE cellular standard, sending video and high-res images became a matter of maximizing the use of the spectrum and optimizing for better data transmission, said Giard.
During the beta period, there was some initial confusion about the network’s capabilities. “‘Oh my gosh, I get broadband Starlink on my phone now,’ [some customers believed] and it’s really not the case,” he said. “This is an entirely separate constellation of satellites that’s dedicated to … working on your phone.”
He also attributed the new capabilities to Apple and Google’s work at the operating system level, emphasizing that developers can tie into existing Application Program Interfaces, or APIs, to make their apps work with T-Satellite.
Importantly, Giard said that T-Mobile is not imposing any data caps or network throttling for T-Satellite customers who make heavy use of the service. “I don’t want to take anything off the table at this point,” he said, “but right now, what we’re launching [today] doesn’t have a data cap.”
In addition to built-in apps such as Apple Maps, Google Maps, Apple Music and Samsung Weather, that were added in September, T-Mobile announced the following list of apps that are working with T-Satellite: T-Life, AllTrails, AccuWeather, CalTopo and onX (plus X and WhatsApp).
As for which apps get optimized next for T-Satellite, Giard says he’s looking forward to what developers and customers start asking for. “Our driving mantra here is … what are we doing next? What pain point are we solving?” he said. The apps coming next “will be the ones that the customers tell us they really want, and [others that] are organically adopted along the way.”